Fancy having a garden, but don’t have a massive space for your crops? Perhaps you live in an apartment building or have a small backyard and need to find a way to get the most out of your limited space.
Well look no further than hydroponic gardening as this is the most space efficient gardening method. You can grow plants vertically, stacked on shelving, indoors in a garage, and in any other unused space.
Before we show how hydroponic gardening works, lets understand what hydroponic gardening even is.
What Is Hydroponic Gardening?
Hydroponic came from the greek words “hydro,” which means water and “ponos,” which means labor. Unlike traditional gardening where plants are grown in soil, hydroponic gardening uses the water-based, soil-less method.
At first, it might seem impossible to have a plant grow without soil. It is even more perplexing when you learn that plants can grow bigger, faster, and stronger in hydroponics compared to soil gardening.
However, hydroponics has been around for quite some time.
The hydroponic gardening method dates back to the ancient world, as seen in the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. This method has been further enhanced by technology and man-made nutrients. In fact, through aeroponics, even NASA proved that plants could grow in outer space.
How Does Hydroponic Gardening Work?
Hydroponic gardening is where the plants receive the nutrients they need directly from the water instead of the soil. The hydroponic plants will sit in a growing medium to hold them upright such as hydroton as opposed to soil. Nutrients, and occasionally oxygen, are added to the water as it flows and is made available to the roots. Plants still need light so they can either grow outside in the sunlight or indoors using a grow light.
Hydroponic plants will grow quicker compared to their soil counterparts as the nutrients are easier to absorb from the water.
Hydroponic gardening allows you to control the environment of the plants. For this reason, plants are lesser prone to diseases compared to their counterparts grown in soil. By completely eliminating environmental factors that can damage your plant, you can have the assurance that you’ll harvest healthier and higher quality crops.
Not to mention you are providing the roots with liquefied nutrients from the water so you can expect faster growth and higher yields.
Hydroponic Equipment
You can plant almost any vegetable or fruit in a hydroponic set up. Now, you don’t need to get your hands dirty to harvest the “fruits of the earth.”
The whole system is also mobile, making it possible for you to move from one place or another to protect them from harsh weather like storm or frost.
The key difference to hydroponic gardening is the equipment and tools used to make the setup work. Here are some of the tools that are usually used:
- Grow light. Sunlight is still the best source of light for the growth of plants. Vegetables, in particular, need a minimum of 6 hours per day of direct sun to propagate. Windowsills are the best areas to germinate seeds and grow your plants. In cases where you can’t meet this requirement, opt to use grow lights.
- Substrate or Medium. You can use substrates like coconut coir, gravel, peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite in place of soil. Other alternatives include rockwool and expanded clay aggregate also know as hydroton. However, you still need liqufied nutrients in the water as these substrates do not provide any nutrients to the plants.
- Water. Try to avoid using chlorine or chemically treated water as these can potentially damage your plants. Ideally you want to use mineral or spring water. However, you can simply use filtered water or reverse osmosis water and add your nutrients to the water.
- Micro and macronutrients. Pre-mixed hydroponic nutrients are now readily available in the market that come in liquid bottles. Nutrients also come in dry form where they are typically more cost efficient per weight but require thorough mixing and testing before adding to your hydroponic systems.
- pH meter. You need to ensure that your nutrient solution is neutral which typically means in the pH range of 5 to 7. Most plants prefer to have water that is around pH 5.5 to 6 which allows them to absorb the most nutrients possible. If your water is too acidic (ph 0 to 5) or alkaline (ph 8 to 14) then your plants will not absorb all the nutrients they need.
- Net pots. These are pots that hold your plant with slits or holes near the bottom to allow the roots to grow. There are simple DIY net pots using plastic cups with holes cut in the bottom which allows the water to flow past the roots.
There are other tools that you may need for your setup such as a water pump or air stone but these 6 items are the fundamental tools that you need to setup any hydroponic system.
Simply put:
Hydroponic gardening = Hydroponic system + nutrients + medium + light source + plant
What Are The Types Of Hydroponic Gardening?
There are several options if you choose to dive into hydroponic gardening. But all these types boil down to two main types of hydroponic gardening: Active Systems and Passive Systems.
Active System
The active system of hydroponic gardening operates using air and water pumps, tubing, and water reservoirs.
Using this system, water with the nutrient solution is pumped through a series of tubes to circulate in various plants. This means that less water is consumed as it’s recycled continuously.
Plus the water is oxygenated as it moves which is needed for the roots to grow. These active systems have been shown to be more efficient especially on large-scale farming.
NFT or Nutrient Film Technique
NFT or Nutrient Film Techniqueuses an active system in gardening where nutrients from the reservoir is pumped into a water channel.
As the nutrient solution moves past the plants, the roots absorb nutrients and water while the rest of it goes back into the reservoir. An air stone is typically placed in the reservoir to oxygenate the water as it gets recirculated in the system.
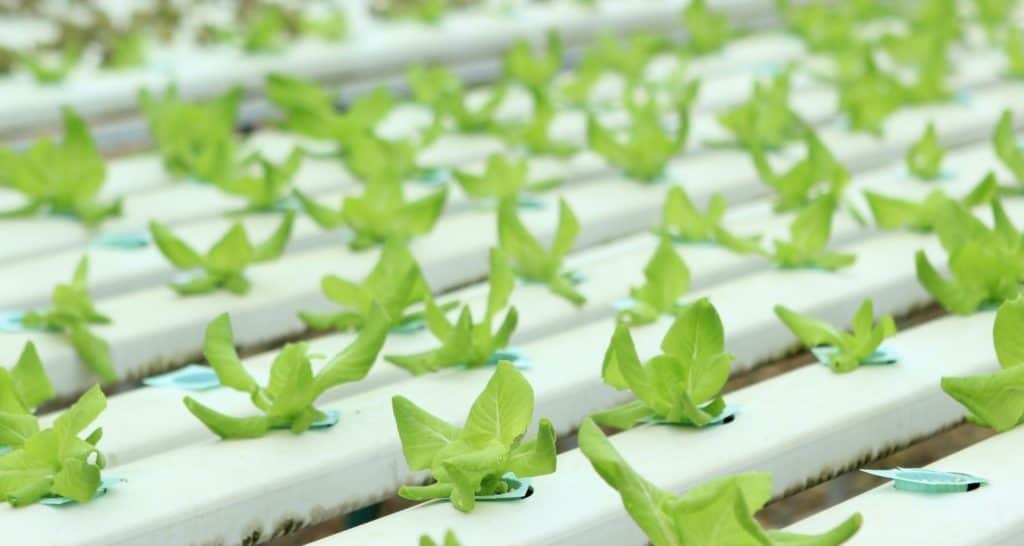

The best plants to use in this method are plants that have a shorter crop cycle. You don’t want plants that take a long time to grow before fruiting such as tomatoes since the long or big roots can clog the channels.
Some examples of good plants for NFT systems are herbs, spinach, and strawberries.
Equipment needed for NFT systems:
- Water reservoir
- Water pump and tubing
- Drain tube
- Timer
- Channel
- Net pots
- Plants
Deep Water Culture
The deep water culture (DWC) system is the simplest and cheapest among all active hydroponic systems. You can use an old aquarium or plastic container as a water reservoir.
The DWC system lets the roots dangle into the nutrient solution. And the air pump creates bubbles in the nutrient solution to provide oxygen for the roots. Oxygenation is crucial as plant roots can drown and die without oxygen.
A common setup for DWC involves using a 5 gallon bucket and drilling a hole in the bucket lid for the net cup. Simply fill the bucket up with nutrient solution, drop your air stone in the bucket, and close the lid. Now just add the plant into the net cup and ensure that the water level stays near the starting level.
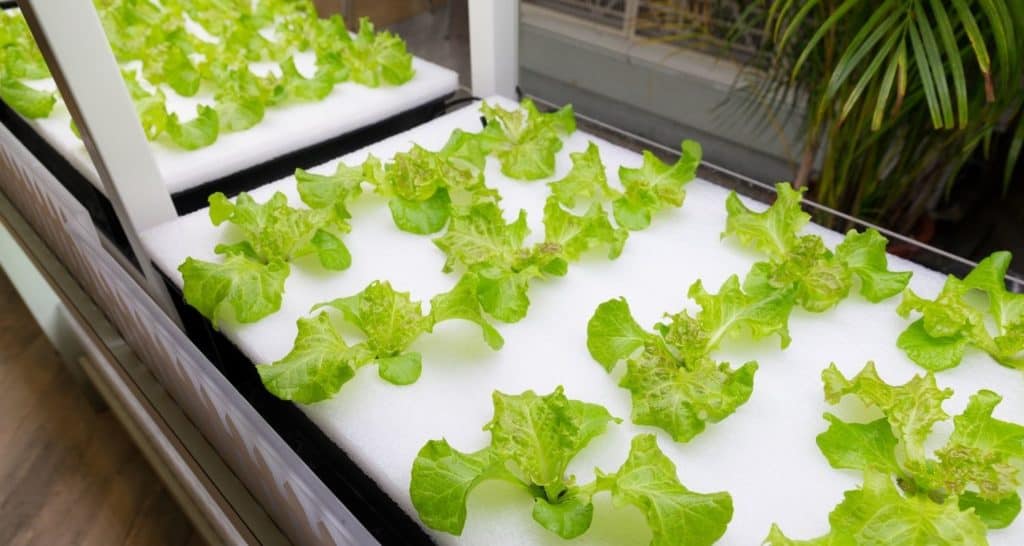

Another common setup for DWC involves styrofoam sheets as this allows your plants to continuously sit right at the water level. Similar to the 5 gallon bucket DWC setup, you simply place your plants in holes or slits in the styrofoam. The rest is just having a water reservoir filled with nutrient solution and having air stones that create bubbles in the water.
Similar to NFT, the best plants to use in this method are plants that have a shorter crop cycle.
Plants with longer crop cycles will grow too tall and may fall over or have their stems break. Unlike growing in soil, the roots of these plants are not grabbing onto anything which means a tall plant can easily fall over if not supported.
Equipment needed for DWC systems:
- Water reservoir
- Air pump
- Airline tubing
- Airstone
- Water pump and tubing
- Styrofoam sheets
- Liquified nutrients
- Net pots
- Plants
Ebb and Flow
The Ebb and Flow, also known as Flood and Drain, is an intermediate setup where the plants sit in a tray that periodically gets flooded with nutrient water. This allows the plants to get watered and fed on a regular basis.
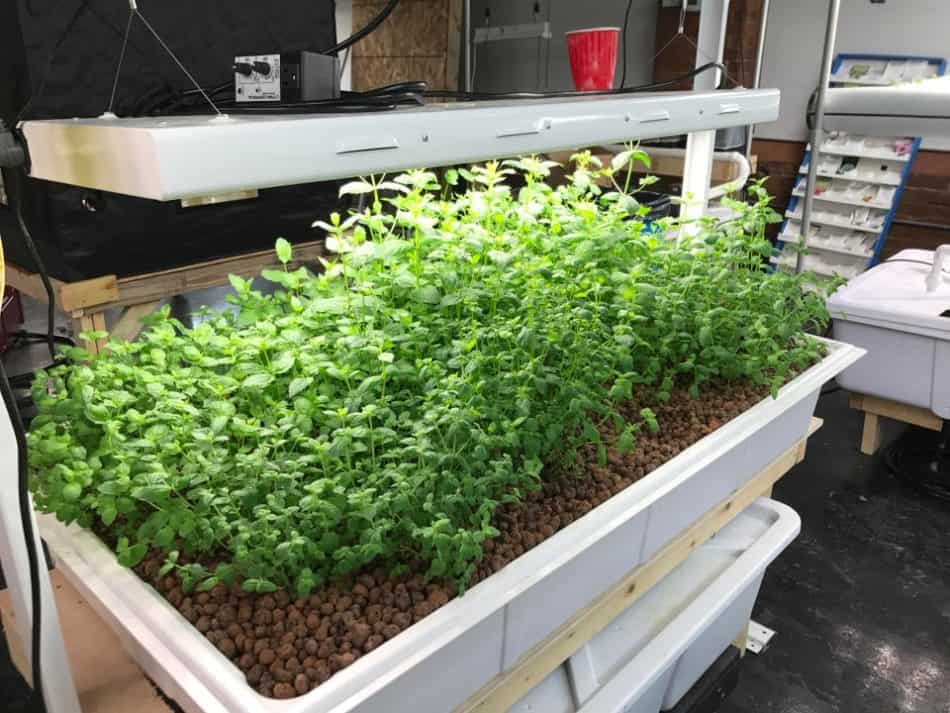

This system is a little more complex than the previous ones as it involves a timer in order to periodically turn on a water pump to flood the container. However, after setting this system up, the ebb and flow method is very hands off and allows for plants to grow at different growth stages.
Depending on the tray size, larger plants can be grown in an ebb and flow system since the growing medium acts as soil. The plant’s roots can grab onto the growing medium which prevents the plant from falling over as it grows taller.
Equipment needed for Ebb and Flow systems:
- Water reservoir
- Water pump and tubing
- Drain tube
- Electrical switch timer
- Growing medium such as hydroton
- Liquified nutrients
- Net pots
- Plants
Aeroponics
The aeroponic system requires more technical know-how as it has the most high-tech equipment amongst the active hydroponic systems.
Similar to the NFT method, the roots dangle in the air with aeroponics. However, the roots absorb the nutrients through the mist from water nozzles rather than direct contact with the liquefied solution.
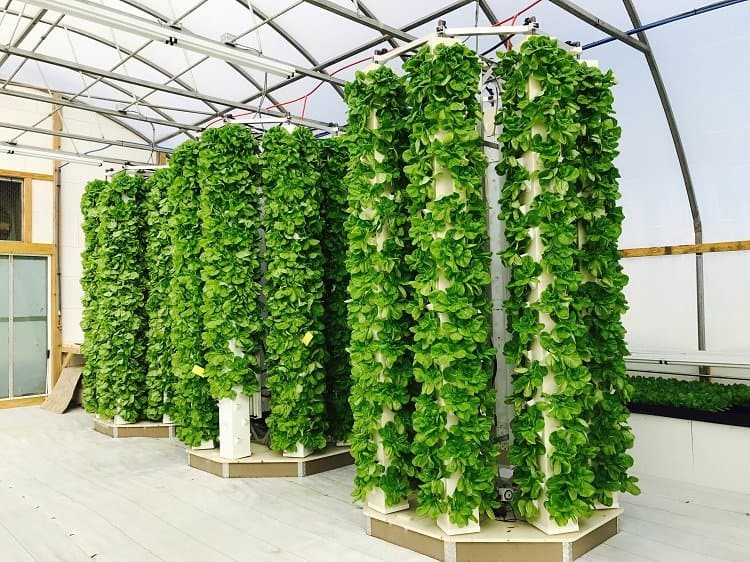

Aeroponics is one of the most, if not the most efficient methods for growing vegetables. The yields are the highest, grow cycles are the shortest, and the water usage is the lightest of all the methods.
However, for all the benefits of aeroponics, there are equally huge challenges as well.
Aeroponics is the most expensive system to set-up and maintain because of its dependence on electricity. Your entire crop can die or get severely damaged if the misters or water pump get clogged. Even worse is if the electricity shuts off since this will kill your crops as well unless you have a generator to keep your system running.
Unlike having plants in soil or water, the aeroponics method has the plant roots exposed to air which means they can dry out quickly which can damage or kill the plant.
You can grow almost any plant in an aeroponics system, however, you want to grow plants that have shorter crop cycles. So leafy greens, herbs, and strawberries are great in this system. However, you can also grow plants with longer cycles such as tomatoes and potatoes in this system.
Just be sure to not grow perennial plants in this system since large or expansive roots can block the sprayers which can cause issues for your plants. As long as the sprayers can create the mist inside the root area then your plants will thrive in this system.
Equipment needed for aeroponic systems:
- Water reservoir
- Water pump and tubing
- Sprayer/misting head
- PVC pipes
- Liquefied nutrients
- Net pots
- Plants
Aquaponics
The aquaponic system is a combination of aquaculture and hydroponics. Aquaponics is where a simple ecosystem is created between the plants and fish.
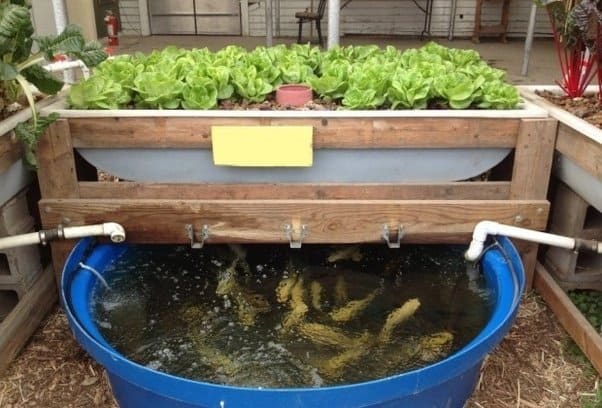

As the fish grow and are fed fish food, they produce waste which is consumed by the plants’ roots. This helps clean the water for the fish and helps the plants grow. This cycle continues until the plants or fish are ready for harvest.
This creates a win-win situation for the plants and fish since they both get to live in an environment that helps them grow. Aquaponics systems also provides both fish and vegetables for consumption. However, you can grow fish such as koi that are more decorative than edible.
The downside to aquaponics is that this system requires you to now raise and feed fish. So this system can be more involved than other active systems since you now have to worry about taking care of fish. This can also increase the cost of setting up and maintaining a hydroponic system.
You can grow almost any plant in an aquaponics system. Similar to an Ebb and Flow system, you will likely have your plants sitting in a growing medium within a garden bed. This means you can grow vegetables with long harvest cycles and plants that can take years to grow. So this system provides the most plant flexibility.
The most commonly used fish for aquaponics are tilapia, blue gill/crappie, catfish, carp, koi, goldfish, pacu, and ornamental fish such as angelfish or tetras.
Equipment needed for aquaponics:
- Water reservoir
- water pump
- Fish tank with pre-drilled holes
- Filter tanks with pre-drilled holes
- Fishnet
- Raft tanks
- Plant rafts
- Liquefied nutrients
- Air blower or pump and aeration components
- Net pots
- Plants
- Fish
Passive System
The passive system has a simplified approach as it doesn’t use any pumps. This means if the electricity goes out that your plants will still survive. Liquefied nutrients are also measured at the beginning and typically are not refilled or reused like the active systems.
Kratky Method System
The Kratky Method is very similar to DWC or deep water culture, where roots have direct contact with the water solution. However, with Kratky, you don’t use air pumps.
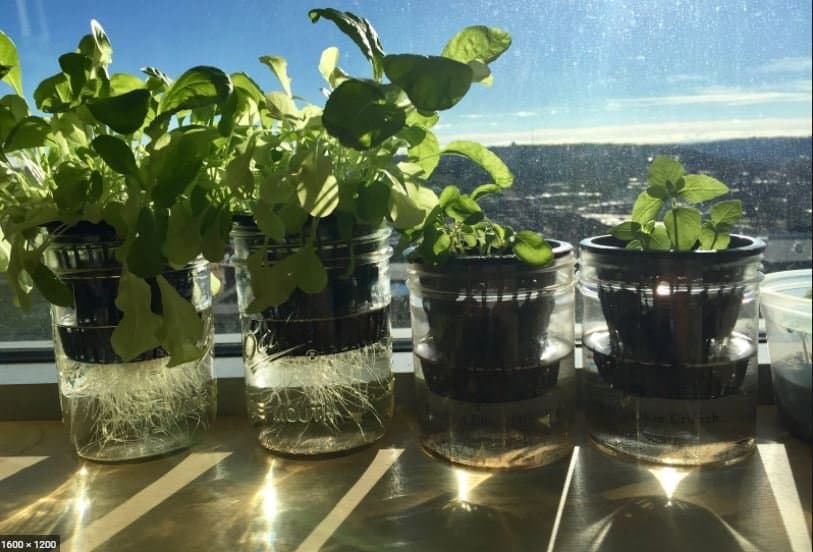

In the Kratky system, you simply let the plant drink the water which means the water level will decrease over time. As the roots continue to grow down into the water, there will be more of the roots that are exposed to air. This is how the plants get the oxygen they need in the kratky system as opposed to air pumps and air stones.
The kratky method is the easiest and least expensive to setup for hydroponic growing. This method is also known as the Set It and Forget It method as you can literally do just that.
You can be completely hands off with this growing method as long as your water reservoir is large enough for the plant you are growing.
Equipment needed for the Kratky Method:
- Water reservoir
- Growing medium
- Liquefied nutrients
- pH measurement tools and control kit
- Seedlings in Net pots
Wick System
The wick system is another very simple system that does not require any electric pumps.
Similar to the Ebb and Flow system, the wick system usually has a grow tray that is above the water reservoir. Instead of water pumps flooding the grow tray, the wick system uses wicks, such as cotton rope, to pull the water up from the reservoir.
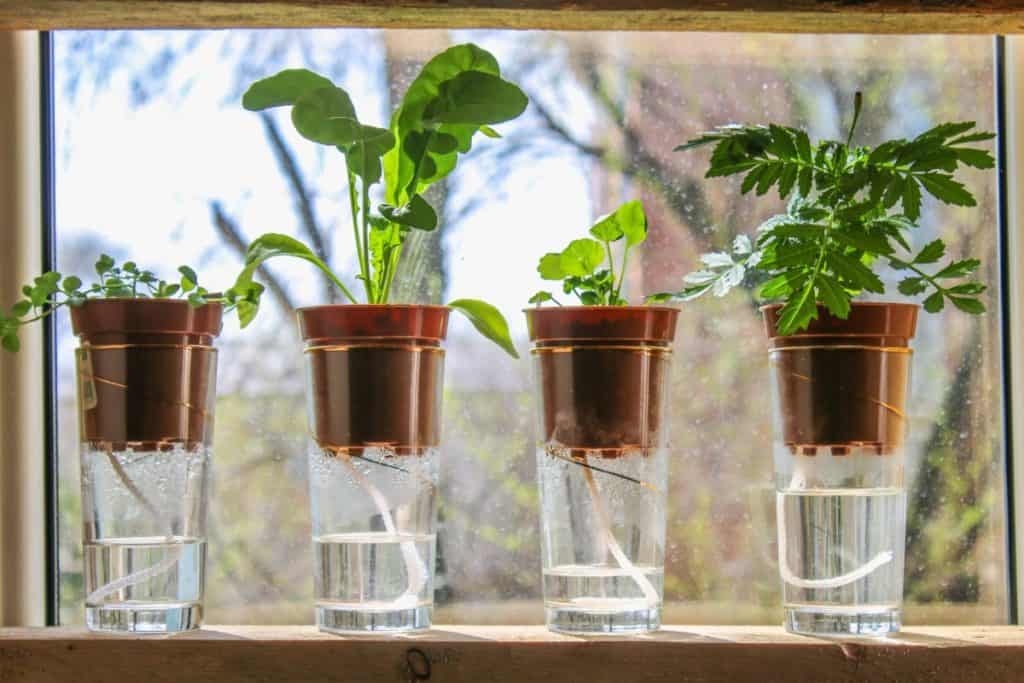

The benefit of the wick system is that you can plant multiple plants in the grow tray and have plants at different growth stages. The plants nearest the wicks will pull up more water if they’re thirstier than the other plants.
The downside to the wick system is that you are limited to the types of plants you can grow in this system. Plants that consume lots of water such as tomato plants will not do well in a wick system since these plants need more water than can be pulled up by the rope. Capillary action works but does not work very fast.
Plants such as herbs and lettuces do well in this system as they are fast growing and don’t require lots of water.
Equipment Needed for the Wick System:
- Water reservoir
- Nutrients
- Cotton or nylon wick
- Substrate such as hydroton
- Seedling
- Growing tray
Tips For Hydroponic Gardening
Regardless of which hydroponic system you decide to use, here are a few tips that will help your plants thrive. Keep in mind you can have multiple hydroponic systems running at the same time. So you do not have to choose just one system and stick to it for all your plants.
DIY Applications
Hydrophonic Gardening can become an expensive hobby to setup. If you don’t have grow lights, pumps, and nutrients laying around then these are all things that you can purchase.
However, hydroponic gardening doesn’t have to be expensive. You can use whatever you have lying in your house as a substitute especially if you have a small personal garden.
Here are some great money saving tips to get started with hydroponics:
- Instead of buying net pots, use plastic cups with holes at the bottom.
- Mason jars are also a great alternative when using any of the passive hydroponic method. Ensure that you cover clear containers with aluminum foil or something that block light to avoid algae from growing inside your water reservoir.
- For aeration, opt to use equipment in your aquarium like pumps, valves, and airline tubing.
Ideal Temperature
The ideal temperature for hydroponic is between 68 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit. For areas where you don’t meet the desired temperature, you can use a heating mat and artificial light to help plants propagate.
You can also grow plants on windowsills, closets, garages, or really any available space that you have within your home. Since your home is insulated, the plants will do well growing in your stable home temperatures.
Ideal pH Level
The ideal pH level for plants is from 5.5 to 6.5. The pH level affects a plants ability to absorb nutrients from the water that are needed for the plant to not only grow but thrive.
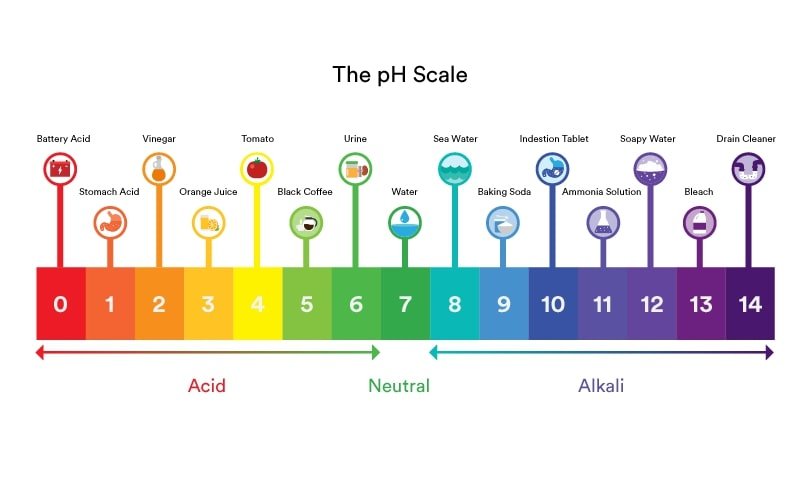
Use a simple pH meter to measure how acidic or alkaline your water is after you add your nutrients. You can get pH meters for as low as $20 online.
If your pH level is below 5.5 or above 6.5 then you can use “pH up” and “pH down” products that many hydroponic nutrient companies sell. However, you can also just add baking soda to increase the pH and plain white vinegar or lemon juice to lower the pH
Maintenance
Check your hydroponic reservoir every 2-3 weeks to ensure the pH is in the 5.5 to 6.5 range and that the PPM is around the 400 to 800 range. This ensures that there are enough nutrients in the water and that the pH is at the right level so the plants can absorb all the nutrients possible.
If you are using an active hydroponic system then its recommended to clean and refill the hydroponic reservoir every 2-3 weeks. This way you can ensure there are not nutrient buildups in any of the plants or pumps.
Easy Hydroponic Plants
Its best to start with some easy plants that grow very well in hydroponic systems. This will ensure that your system is setup properly so that you can then grow other plant types.
Here are 10 best plants to grow in a hydroponic system:
- Lettuce
- Spinach
- Strawberries
- Bell Peppers
- Bokchoy
- Tomatoes
- Celery
- Cucumber
- Microgreens
- Herbs selection include basil, chives, cilantro, dill, mint, oregano, parsley, rosemary, thyme, and watercress.
Growing Hydroponically
Hydroponic gardening is one of the most efficient versions of sustainable gardening. Hydroponics is becoming more widespread as the world thinks about how to produce more food to feed our growing population.
Now people can grow plants indoors, on balconies, rooftops, and even warehouses. This allows anyone to have access to fresh produce that can literally go from “farm to table” in seconds. There are no preservatives needed, no pesticides used, and smaller carbon footprint created by eating this way.
The best time to get started in hydroponic gardening is right now as you will only get better with more trial and error.
You will start to find vegetables and fruits you enjoy growing and eating. Moreover, you’ll be surprised by how good your own fresh produce tastes. Not to mention, your friends and family will be sure to snack on your fresh produce everytime it’s harvest time.
Comment down below your favorite hydroponic method along with the vegetables and fruits you typically grow in that method.

